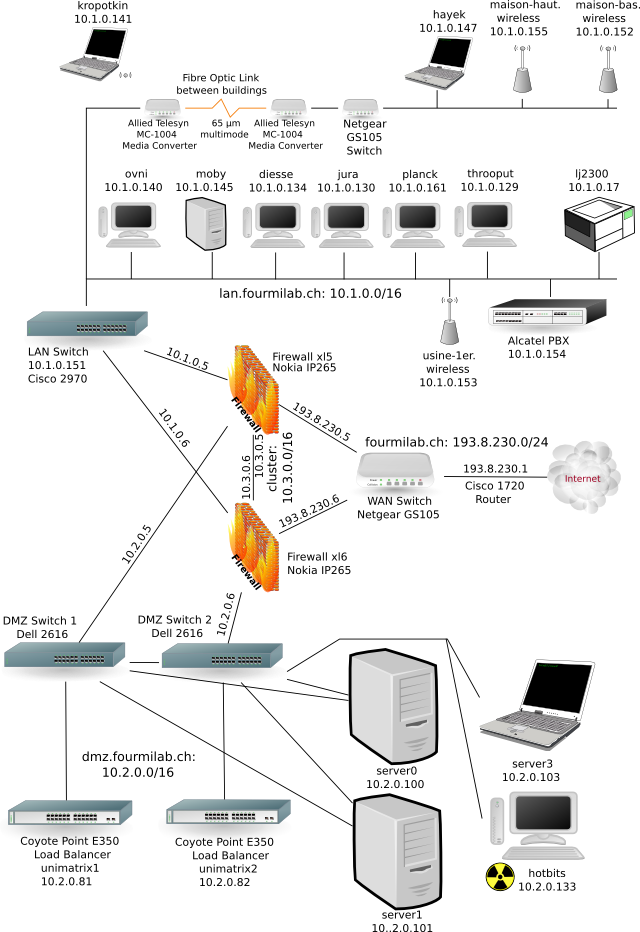
Salt Spray Adventures requires a Wide Area Network that includes an Intranet where each employee must have a personal account to access their emails and the server that manages their accounts.
Since there are three locations where tour guides must access their intranet that are across town, it's important that connection to their Internet Service Provider is available at each location either by cable or by wifi.
This will enable cheap access for tour guides to be in contact with the office regardless of whether they area the boathouse or at the lighthouse.
Please see the diagram below includes all protocols, software, transmission mediums and hardware device required for this solution. Please note that wifi is available in all three locations to allow the tour guides to continue to use their tablets.
Students who thought Optical Fibre backbone dug into the streets of Byron Bay for over 2km was a reasonable solution need to look at these videos that offers a distinction between a LAN and a WAN:
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fCxfp1iUbqw
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jchxjL92uaw
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=n1B_dz7N6K4